Read the paper: QCD-10-037
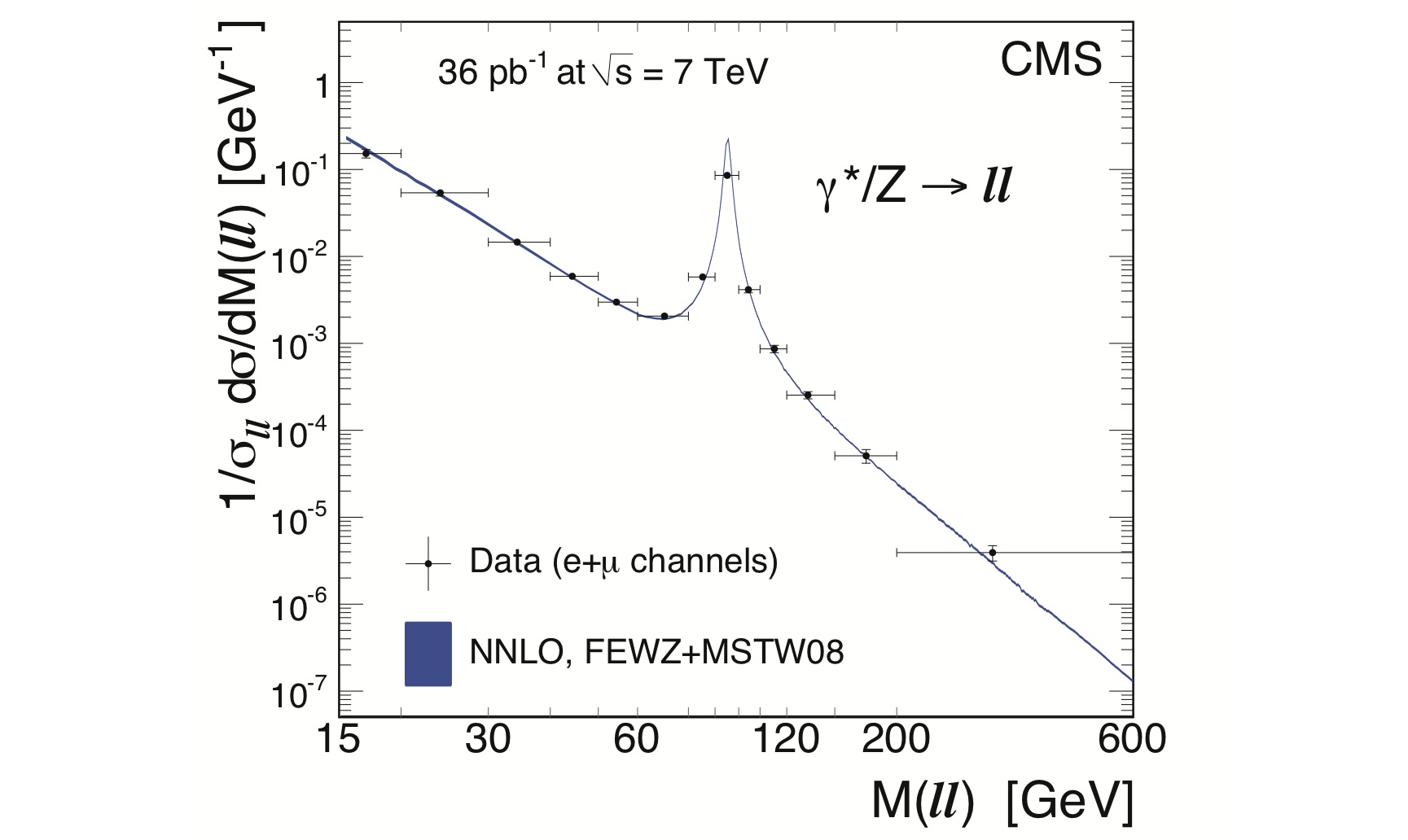
The measured Drell-Yan production rates, normalised to the production rates in the Z-boson region, show good agreement with the theoretical predictions.
The Drell-Yan process occurs when a quark from one of the colliding protons annihilates with an anti-quark from a proton travelling in the opposite direction and is converted into a photon or a Z boson, which decays into two leptons. Studying this process is very important because:
- Comparisons between theoretical calculations and experimental measurements provide stringent tests for the theory of perturbative Quantum Chromodynamics (pQCD).
- Comparisons also provide significant constraints on the evaluation of parton distribution functions (PDFs).
- It is a key background in the searches for new phenomena, including searches for the Higgs boson.
For this paper, the data samples chosen were ones in which the photon or Z boson formed from the quark annihilation decayed into pairs of electrons or muons.
Group: Electroweak Physics (EWK)
Collisions: pp
Centre-of-mass energy: 7 TeV
Data sample: 35.9 ± 1.4 pb–1
Dates of data collection: 2010
Measurement/Limit:
Di-lepton invariant mass (Mll) range covered: 15–600 GeV
Submitted to: Journal of High Energy Physics (JHEP)
- Log in to post comments

