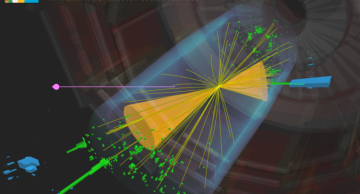
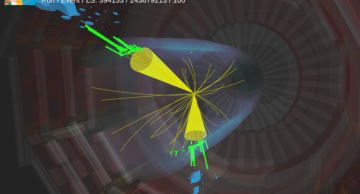
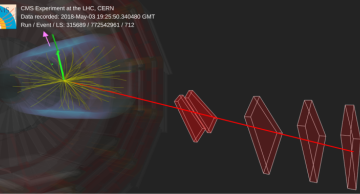
The CMS experiment utilises cutting-edge machine learning techniques to search for microscopic, quantum black holes and other exotic objects that evaporate in an instant.
Black holes are amongst the most fascinating objects in the universe.…
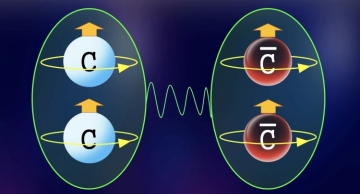
Upon close inspection, the tetraquark family members are consistent with tightly bound diquark pairs
The CMS Collaboration has identified three extremely rare same-flavor teraquark states and determined, based on their spin-parity configuration,…
Using data collected from 2016 to 2023 and cutting-edge machine learning, CMS observes for the first time the creation of a top quark together with a W and a Z boson – a process so rare it occurs only once in a trillion proton-proton…
In the first search of its kind at a particle collider, the CMS experiment looks for partially visible sprays of particles (jets), containing leptons and dark matter using physics-informed machine learning.
Can we shed light on dark matter?…
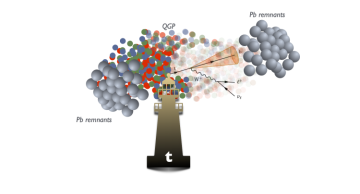
Five years after the first evidence that heavy metal hits the top quark, CMS now observes the clash of two titans with higher precision at unprecedented energy.
Using lead-lead collision data acquired in 2023 at the highest energy ever achieved by…
CMS scientists are on the hunt for a new, heavy particle that decays into a pair of Higgs bosons. Using the final state with two bottom quarks and two tau leptons, the search sets the most stringent limits to date in the mass range 1.4–4.5…
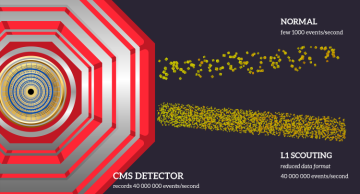
The CMS experiment is utilising a novel technique called L1 Scouting, which allows it to record data from all collisions, without any selection, but in a reduced format. A first pioneer physics result using this data showcases the immense…
CMS observes collective motion of particles in light-ion collisions, providing robust evidence of how initial nuclear geometry maps to final-state flow.
For the first time, the CMS experiment has measured how particles flow in collisions of…
The CMS experiment has analyzed the first-ever neon-neon collisions, looking for signs of quark-gluon plasma. By comparing these results with data from oxygen-oxygen, xenon-xenon, and lead-lead collisions, physicists find an interesting…
CMS scientists study the first-ever oxygen-oxygen collisions at the LHC, and observe signs of quarks and gluons losing energy when they travel through quark-gluon plasma – a state that existed just after the Big Bang.
When heavy ions such as…
Turning the LHC into a photon collider, the CMS experiment observes for the first time how two photons fuse and convert into two W bosons. Stringent limits are set on parameters that would describe possible deviations from the standard…
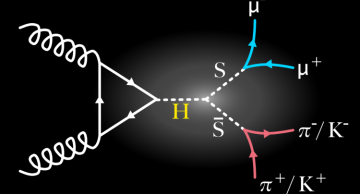
In a first search of its kind at the LHC, the CMS experiment looks for light beyond-the-standard-model particles with a mass in the GeV range that decay into charged hadrons and muons. It establishes that if they exist, they would be produced…