Nowadays, artificial neural networks have an impact on many areas of our day-to-day lives. They are used for a wide variety of complex tasks, such as driving cars, performing speech recognition (for example, Siri, Cortana, Alexa), suggesting…
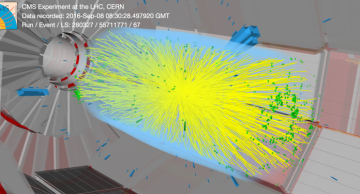
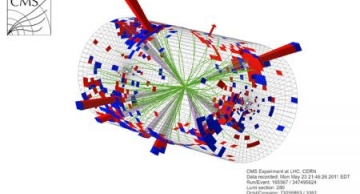
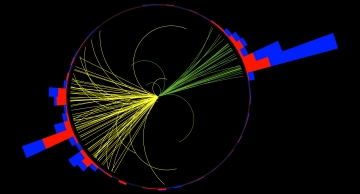
When the CMS experiment records particle collision events, a large number of unwanted extra collisions overlap in the detector and hide the rare particle collision that is worthwhile studying. CMS physicists have developed a new method that…
New algorithms from the Compact Muon Solenoid experiment use the ideas used in mobile phone facial recognition to better understand the collisions at the Large Hadron Collider.
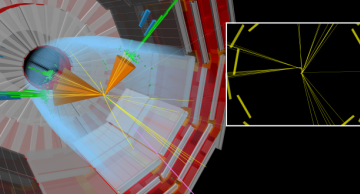
One of the most exciting challenges at the Large Hadron Collider is the…
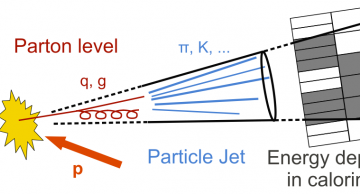
Jets are the experimental signatures of quarks and gluons produced in high-energy processes such as head-on proton-proton collisions. As quarks and gluons have a net colour charge and cannot exist freely due to colour-confinement, they are not…
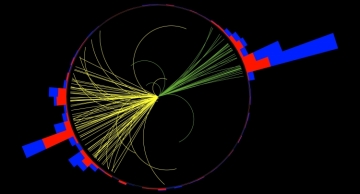
The search for microscopic black holes at the LHC is motivated by the hierarchy problem — the huge observed difference between the strengths of the electroweak and gravitational forces. The ADD model (Arkani-Hamed, Dimopoulos, and Dvali) offers an…
A search is presented for a massive particle, generically referred to as a Z′, decaying into a t-tbar pair. The search focuses on Z′ resonances that are sufficiently massive to produce highly Lorentz-boosted top quarks, which yield collimated decay…
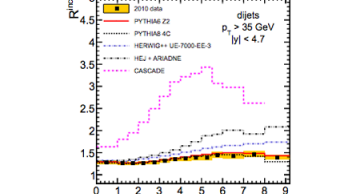
A study of dijet production in proton-proton collisions was performed at √s = 7 TeV for jets with pT > 35 GeV and |y| < 4.7[1] using data collected with the CMS detector at the LHC in 2010. Events with at least one pair of jets are denoted as…