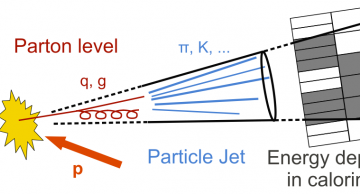
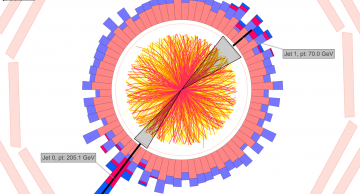
Jets are the experimental signatures of quarks and gluons produced in high-energy processes such as head-on proton-proton collisions. As quarks and gluons have a net colour charge and cannot exist freely due to colour-confinement, they are not…
The search for microscopic black holes at the LHC is motivated by the hierarchy problem — the huge observed difference between the strengths of the electroweak and gravitational forces. The ADD model (Arkani-Hamed, Dimopoulos, and Dvali) offers an…
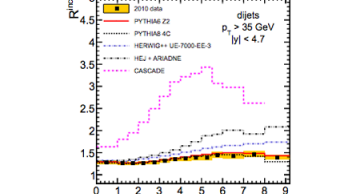
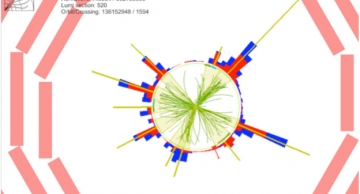
A study of dijet production in proton-proton collisions was performed at √s = 7 TeV for jets with pT > 35 GeV and |y| < 4.7[1] using data collected with the CMS detector at the LHC in 2010. Events with at least one pair of jets are denoted as…
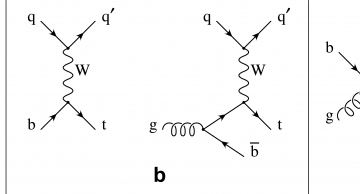
The Top quark is the heaviest of the six quarks of the Standard Model and was discovered only 16 years ago by the Tevatron experiments at Fermilab. In addition to the usual production of Top-AntiTop pairs in accordance with quantum chromodynamics (…
Read the paper: SUS-11-003
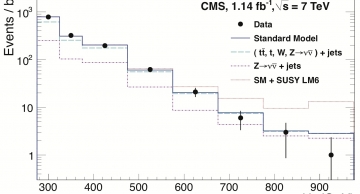
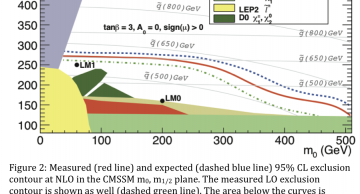
The analysis shows no excess of events over the Standard Model expectations. As a result, exclusion limits were placed on searches for squarks and gluinos in the Constrained Minimal Supersymmetric extension of the Standard…
Read the paper: TOP-11-003
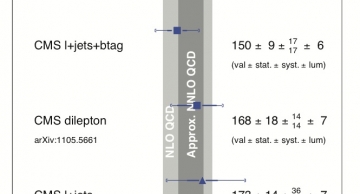
The measured production rates of Top-antiTop pairs, where one lepton and four jets of particles is observed in the final state, show good agreement with Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD), the theory of the strong interaction.…
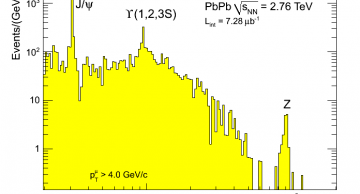
The CMS experiment has made several unique measurements using data from LHC collisions of lead nuclei (PbPb, November 2010) at centre-of-mass energies of 2.76 TeV per nucleon pair.
Phenomena measured for the first time in nucleus-nucleus collisions…
The Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) Collaboration at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has announced the results of the search for supersymmetry (SUSY) in events with jets and missing transverse energy. The search is based on data accumulated by the…
The CMS experiment at CERN's Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has completed a search for microscopic black holes produced in high-energy proton-proton collisions. No evidence for their production was found and their production has been excluded up to a…
After only three weeks of heavy-ion running at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC), the CMS experiment is already yielding new insights into the condition of matter that existed in the very first instants of the Universe’s life, some 13.7 billion…
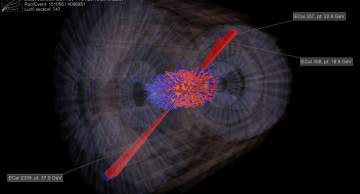
Z bosons produced in collisions of heavy ions have been observed for the first time by the CMS experiment at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC). CMS observed 10 events containing a distinctive candidate Z boson reconstructed from a pair of electrons…